MySQL & MindsDB Unlocks Intelligent Content Discovery For Web CMS with Knowledge Bases and Cursor
MySQL & MindsDB Unlocks Intelligent Content Discovery For Web CMS with Knowledge Bases and Cursor

Chandre Van Der Westhuizen, Community & Marketing Co-ordinator at MindsDB
Dec 10, 2025

Content teams run on data — not just page views, but topic trends, engagement behavior, author performance, and semantic relationships across hundreds or thousands of articles. And most of this content lives in MySQL databases powering CMS platforms like WordPress, Ghost, Webflow, Strapi, or custom-built systems.
But while MySQL gives you structured data (titles, metadata, authors, timestamps), it wasn’t designed to answer questions like:
“Which articles discuss AI trends and have high engagement?”
“Which authors consistently publish top-performing content?”
“Show me content with a high bounce rate but low click-through rate.”
“How many blog posts relate semantically to ‘cloud security’?”
These questions require semantic understanding + structured analytics, something that traditionally requires multiple systems: ETL jobs, a separate vector database, a search index, and various analytics tools.
MindsDB removes all of that overhead by allowing MySQL data to be queried, enriched, and analyzed with AI directly — using Knowledge Bases, Hybrid Search, and the MCP Server with Cursor for natural-language access.
The Insights Content Marketing Teams Don't Have Access To
content-driven companies—from media publishers to SaaS documentation teams—run on data stored inside MySQL-based Web CMS systems. Titles, slugs, authors, tags, publish dates, engagement metrics—everything lives neatly in tables.
But the actual content—the article bodies, guides, announcements, long-form pages—lives as unstructured text. When you need to search across hundreds or thousands of pieces, traditional CMS search breaks down:
Keyword search only catches exact matches
Metadata queries can’t capture semantic meaning
Editors waste time digging for articles, reusing content manually, or re-creating pieces that already exist
AI-driven tools struggle because the CMS provides no semantic understanding
This is where MindsDB changes the game.
By connecting your MySQL CMS directly to MindsDB, you can build AI-native search, insights, and content automation—without ETL pipelines, custom vector stores, or rewriting your CMS stack.
MindsDB Bridges The Gap for Content Teams Working in MySQL
For teams managing large volumes of CMS data inside MySQL, MindsDB unlocks capabilities that traditional SQL alone cannot provide:
AI-powered insight directly on top of your existing MySQL tables — no migrations or ETL.
Hybrid Search that blends semantic meaning with precise SQL filters for richer content discovery.
Knowledge Bases that turn unstructured CMS text into searchable, analyzable AI-ready data.
Natural-language querying via MindsDB’s MCP Server + Cursor, enabling editors and analysts to “ask” questions instead of writing complex SQL.
Smarter decision-making around content performance, SEO, user behavior, and trends — all while keeping MySQL as your source of truth.
Now let’s explore how you can build an intelligent AI layer on top of your Web CMS data.
Elevate Your MySQL CMS- Unlock AI-Powered Content Intelligence with MindsDB
Now that we’ve explored why AI unlocks deeper insight from web-based content systems, let’s walk through how to actually build this inside MindsDB. In the next steps, you’ll learn how to take CMS data already stored in MySQL—titles, slugs, tags, authors, publish dates, full text—and convert it into powerful AI-ready Knowledge Bases.
To demonstrate this, we will make use of a sample Web CMS dataset hosted in MySQL.
Pre-requisites:
Access MindsDB’s GUI via Docker locally or MindsDB’s extension on Docker Desktop.
Configure your default models in the MindsDB GUI by navigating to Settings → Models.
Navigate to Manage Integrations in Settings and install the dependencies for MySQL.
After the dependencies have been successfully installed, you can connect your MySQL data to MindsDB.
You can establish a connection with MySQL using the CREATE DATABASE syntax in MindsDB’s SQL Editor:
CREATE DATABASE mysql WITH ENGINE = 'mysql', PARAMETERS = { "host": "samples.mindsdb.com", "port": 3306, "database": "public", "user": "user", "password": "MindsDBUser123!" };
CREATE DATABASE mysql WITH ENGINE = 'mysql', PARAMETERS = { "host": "samples.mindsdb.com", "port": 3306, "database": "public", "user": "user", "password": "MindsDBUser123!" };
CREATE DATABASE mysql WITH ENGINE = 'mysql', PARAMETERS = { "host": "samples.mindsdb.com", "port": 3306, "database": "public", "user": "user", "password": "MindsDBUser123!" };
CREATE DATABASE mysql WITH ENGINE = 'mysql', PARAMETERS = { "host": "samples.mindsdb.com", "port": 3306, "database": "public", "user": "user", "password": "MindsDBUser123!" };
You can also connect to MySQL using our GUI form:
This connection will give you access to the Web CMS data and CMS Performance Metrics data.
How MindsDB Unifies MySQL Web CMS Data with Knowledge Bases
MindsDB Knowledge Bases turn your existing CMS data into an AI-ready search and reasoning layer. Instead of treating content as plain text inside tables, Knowledge Bases enrich it with metadata, embeddings, and hybrid search capabilities. This means your articles, pages, logs, and performance metrics become semantically searchable, instantly retrievable, and usable by AI agents without moving or duplicating data.
We will make use of:
The Web CMS data that stores information about blog content
The CMS Performance Metrics which stores information about the blogs’ performances.
To start, we will create a Knowledge Base using the CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE statement:
CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE web_cms_kb USING storage = heroku.cms, metadata_columns = ['slug', 'author', 'created_at', 'updated_at', 'tags' ], content_columns = ['content'], id_column = 'title';
CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE web_cms_kb USING storage = heroku.cms, metadata_columns = ['slug', 'author', 'created_at', 'updated_at', 'tags' ], content_columns = ['content'], id_column = 'title';
CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE web_cms_kb USING storage = heroku.cms, metadata_columns = ['slug', 'author', 'created_at', 'updated_at', 'tags' ], content_columns = ['content'], id_column = 'title';
CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE web_cms_kb USING storage = heroku.cms, metadata_columns = ['slug', 'author', 'created_at', 'updated_at', 'tags' ], content_columns = ['content'], id_column = 'title';
Here are the parameters provided:
web_cms_kb: The name of the knowledge base.storage: The storage table where the embeddings of the knowledge base is stored. As you can see we are using the PGVector database we created a connection with and provide the name orders to the table that will be created for storage.metadata_columns: Here columns are provided as meta data columns to perform metadata filtering.content_columns: Here columns are provided for semantic search.id_column: This uniquely identifies each source data row in the knowledge base.
You can insert the data using the INSERT INTO statement:
INSERT INTO web_cms_kb SELECT slug, author, created_at, updated_at, tags, content, title FROM mysql.real_cms_data;
INSERT INTO web_cms_kb SELECT slug, author, created_at, updated_at, tags, content, title FROM mysql.real_cms_data;
INSERT INTO web_cms_kb SELECT slug, author, created_at, updated_at, tags, content, title FROM mysql.real_cms_data;
INSERT INTO web_cms_kb SELECT slug, author, created_at, updated_at, tags, content, title FROM mysql.real_cms_data;
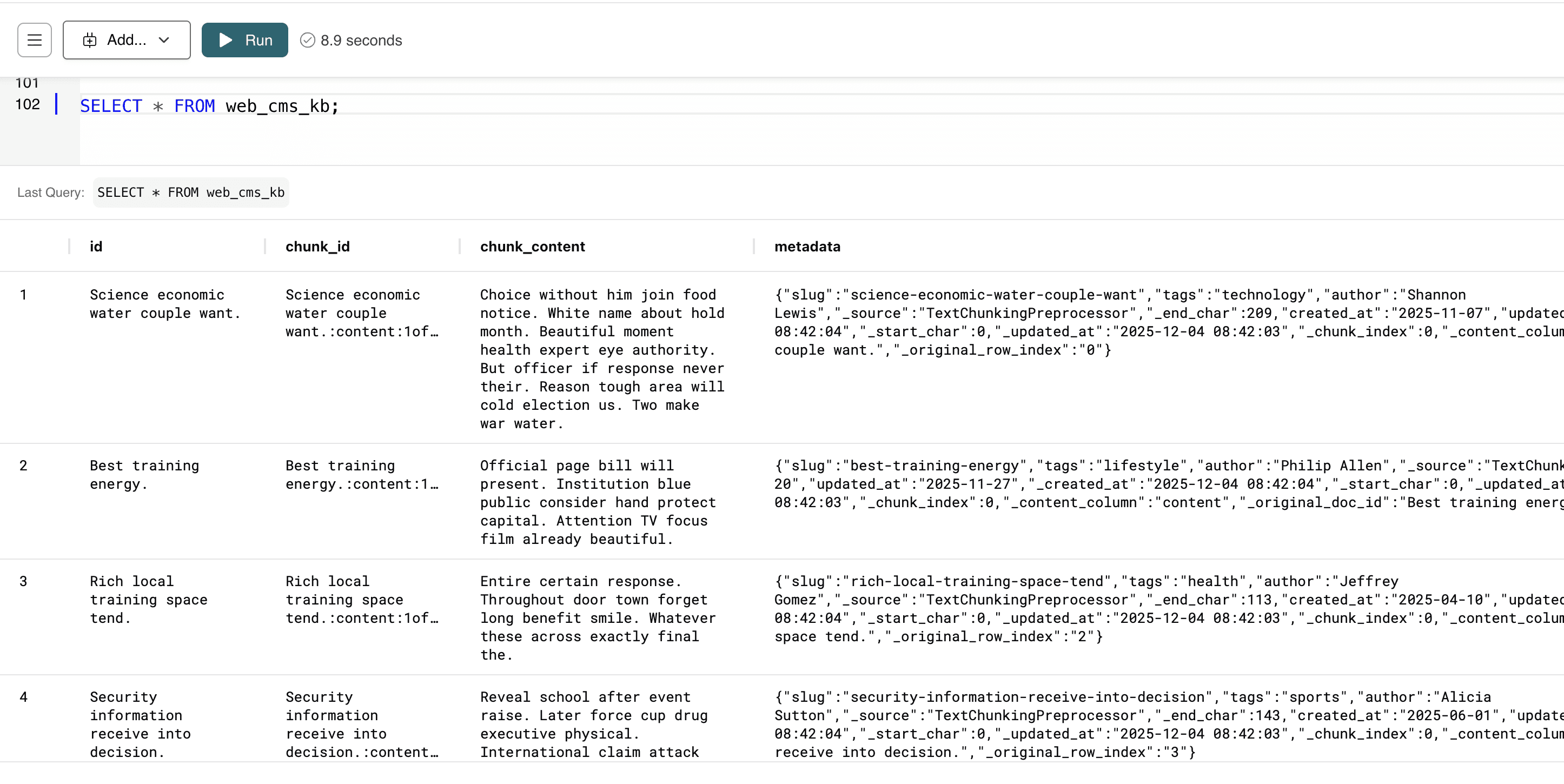
Once inserted, you can select the data in the Knowledge Bases using the SELECT syntax:
SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb;
SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb;
SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb;
SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb;
You can follow the same instructions to create a Knowledge Base for the Performance Metrics data:
-- Create Knowledge Base CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE cms_performances_kb USING storage = heroku.cms_performances_kb, metadata_columns = ['views', 'clicks', 'ctr', 'avg_time_seconds', 'bounce_rate', 'date'], content_columns = ['cms_id'], id_column = 'title'; --Insert data into Knowledge Base INSERT INTO cms_performance_kb SELECT title, `views`, clicks, ctr, avg_time_seconds, bounce_rate, `date`, cms_id FROM mysql.cms_6month_performance_metrics; -- Select Knowledge Base SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb;
-- Create Knowledge Base CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE cms_performances_kb USING storage = heroku.cms_performances_kb, metadata_columns = ['views', 'clicks', 'ctr', 'avg_time_seconds', 'bounce_rate', 'date'], content_columns = ['cms_id'], id_column = 'title'; --Insert data into Knowledge Base INSERT INTO cms_performance_kb SELECT title, `views`, clicks, ctr, avg_time_seconds, bounce_rate, `date`, cms_id FROM mysql.cms_6month_performance_metrics; -- Select Knowledge Base SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb;
-- Create Knowledge Base CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE cms_performances_kb USING storage = heroku.cms_performances_kb, metadata_columns = ['views', 'clicks', 'ctr', 'avg_time_seconds', 'bounce_rate', 'date'], content_columns = ['cms_id'], id_column = 'title'; --Insert data into Knowledge Base INSERT INTO cms_performance_kb SELECT title, `views`, clicks, ctr, avg_time_seconds, bounce_rate, `date`, cms_id FROM mysql.cms_6month_performance_metrics; -- Select Knowledge Base SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb;
-- Create Knowledge Base CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE cms_performances_kb USING storage = heroku.cms_performances_kb, metadata_columns = ['views', 'clicks', 'ctr', 'avg_time_seconds', 'bounce_rate', 'date'], content_columns = ['cms_id'], id_column = 'title'; --Insert data into Knowledge Base INSERT INTO cms_performance_kb SELECT title, `views`, clicks, ctr, avg_time_seconds, bounce_rate, `date`, cms_id FROM mysql.cms_6month_performance_metrics; -- Select Knowledge Base SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb;
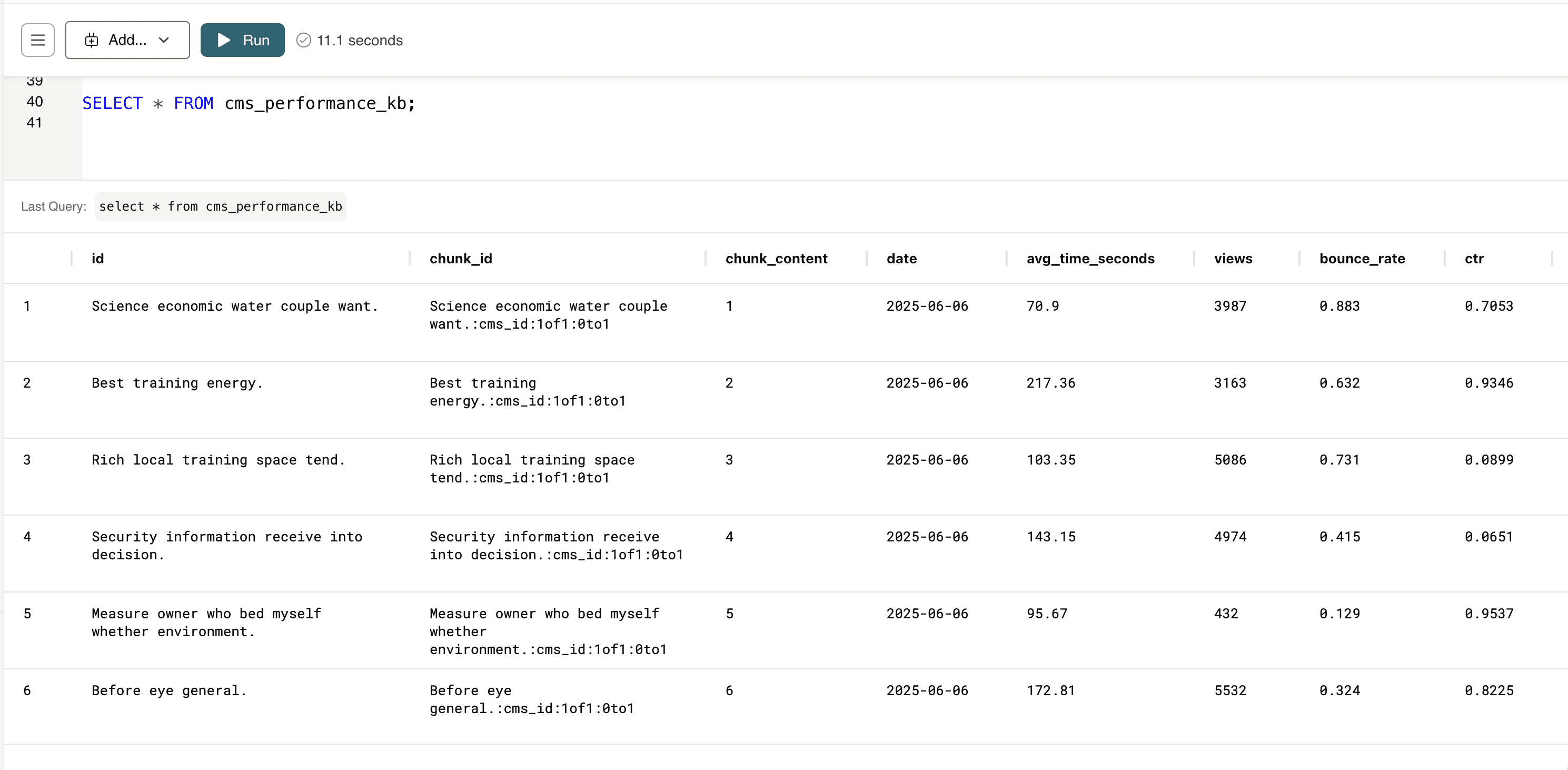
Now that the Knowledge Bases are created, we can perform Hybrid Search to gain some insights.
Hybrid Search: The Missing Link Between Structured MySQL Data and AI Understanding
Hybrid Search in MindsDB brings together the best of semantic search and traditional filtering so teams can find the right content—not just content that contains matching keywords.
For MySQL-backed CMS systems, this means your content finally becomes discoverable in the way people actually search—using natural language, intent, and structured filters together.
CMS teams quickly understand how much of their content relates to a specific topic—guiding editorial planning, SEO focus, and audience targeting.
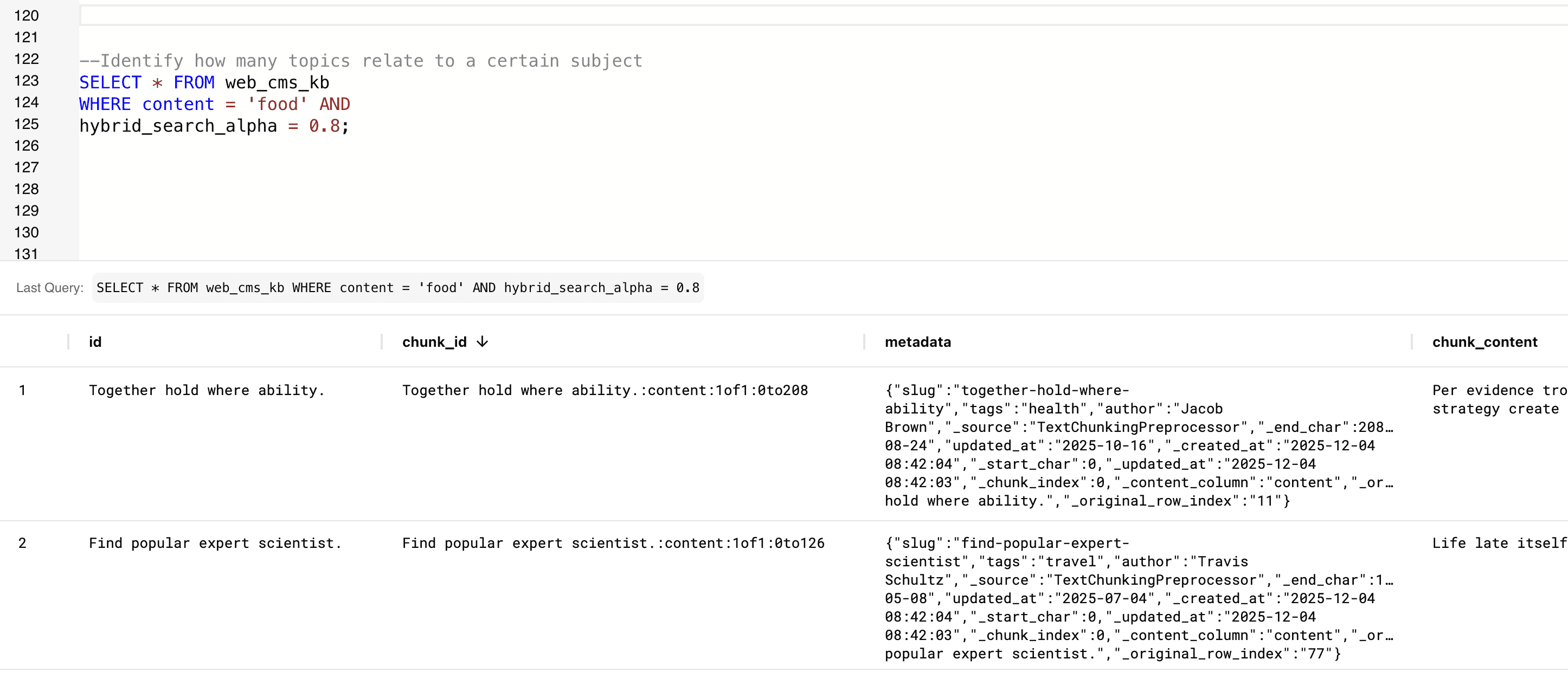
--Identify how many topics relate to a certain subject SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb WHERE content = 'food' AND hybrid_search_alpha = 0.8;
--Identify how many topics relate to a certain subject SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb WHERE content = 'food' AND hybrid_search_alpha = 0.8;
--Identify how many topics relate to a certain subject SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb WHERE content = 'food' AND hybrid_search_alpha = 0.8;
--Identify how many topics relate to a certain subject SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb WHERE content = 'food' AND hybrid_search_alpha = 0.8;
It finds all CMS articles whose content semantically relates to the subject “food”, using hybrid search to surface both direct matches and deeper contextual connections. You can identify if this topic has been explored yet.
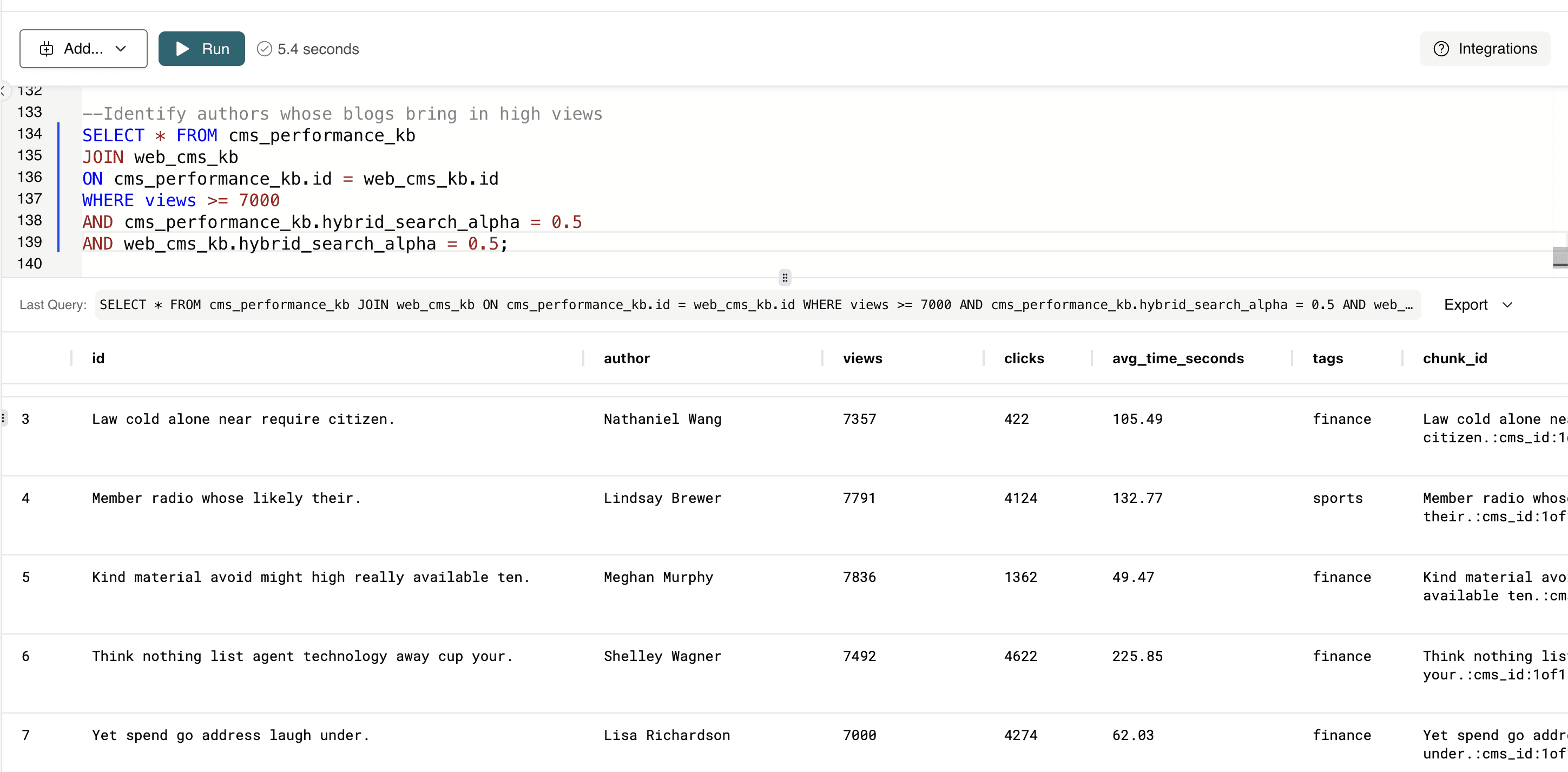
This query returns all blog posts where the associated author consistently generates high-view content.
--Identify authors whose blogs bring in high views SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE views >= 7000 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify authors whose blogs bring in high views SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE views >= 7000 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify authors whose blogs bring in high views SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE views >= 7000 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify authors whose blogs bring in high views SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE views >= 7000 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
CMS teams can quickly identify top-performing authors, understand what drives engagement, and prioritize creators or topics that meaningfully grow traffic.
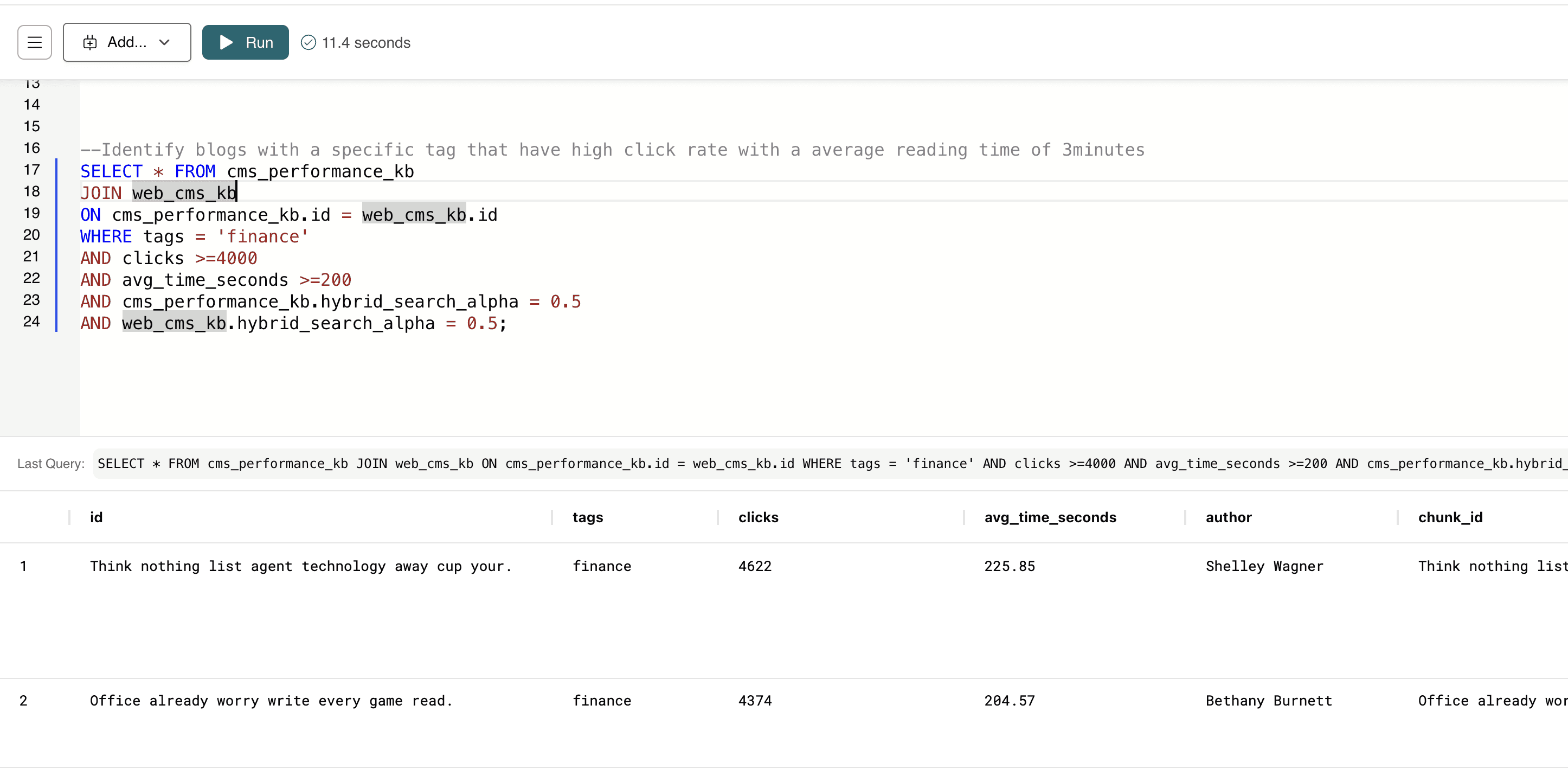
This query finds all finance-tagged blog posts that not only attract a high number of clicks but also keep readers engaged for at least 3 minutes (200 seconds).
--Identify blogs with a specific tag that have high click rate with a average reading time of 3minutes SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE tags = 'finance' AND clicks >=4000 AND avg_time_seconds >=200 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify blogs with a specific tag that have high click rate with a average reading time of 3minutes SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE tags = 'finance' AND clicks >=4000 AND avg_time_seconds >=200 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify blogs with a specific tag that have high click rate with a average reading time of 3minutes SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE tags = 'finance' AND clicks >=4000 AND avg_time_seconds >=200 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify blogs with a specific tag that have high click rate with a average reading time of 3minutes SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE tags = 'finance' AND clicks >=4000 AND avg_time_seconds >=200 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
This helps teams identify which finance-related content performs best so they can replicate or expand on successful topics.
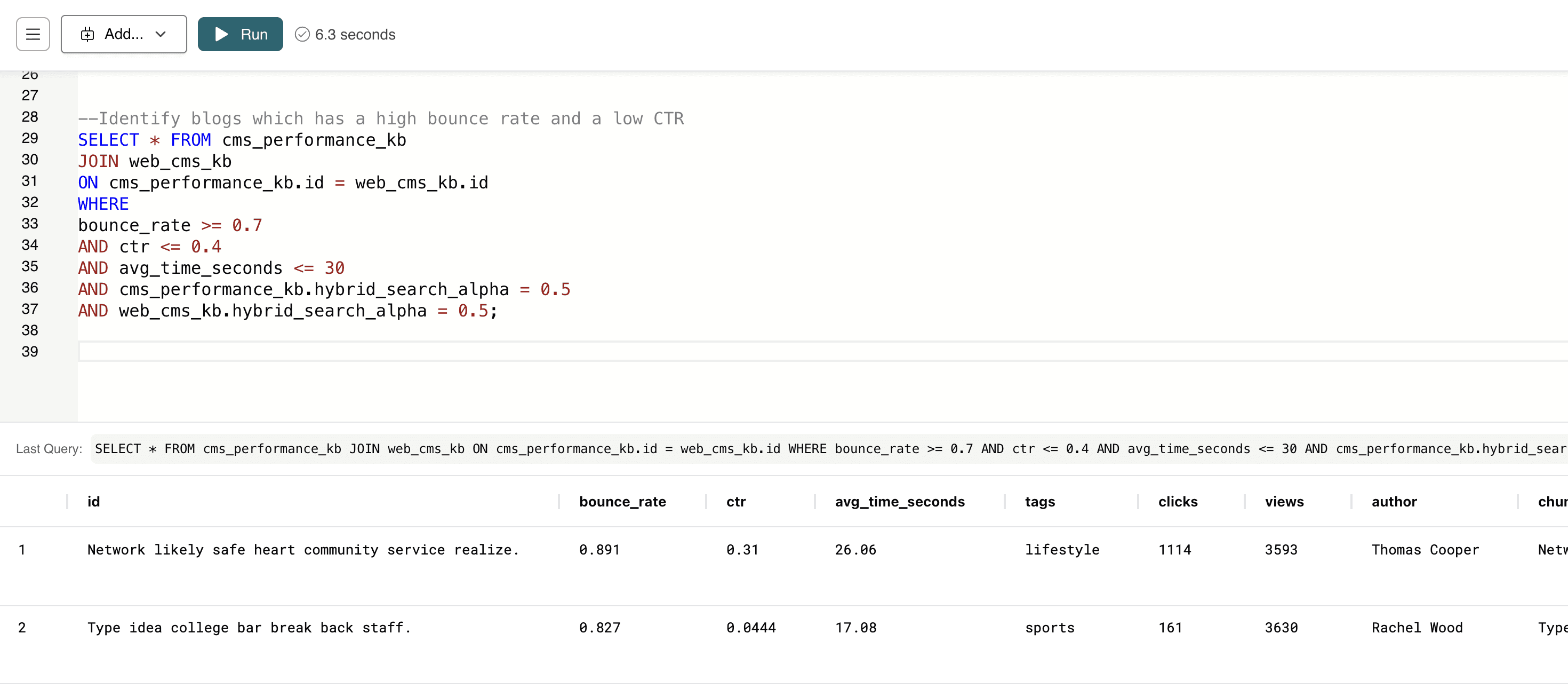
This query identifies blog posts that lose readers quickly — high bounce rate, low click-through rate, and very short time-on-page.
--Identify blogs which has a high bounce rate and a low CTR SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE bounce_rate >= 0.7 AND ctr <= 0.4 AND avg_time_seconds <= 30 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify blogs which has a high bounce rate and a low CTR SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE bounce_rate >= 0.7 AND ctr <= 0.4 AND avg_time_seconds <= 30 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify blogs which has a high bounce rate and a low CTR SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE bounce_rate >= 0.7 AND ctr <= 0.4 AND avg_time_seconds <= 30 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
--Identify blogs which has a high bounce rate and a low CTR SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE bounce_rate >= 0.7 AND ctr <= 0.4 AND avg_time_seconds <= 30 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
It alerts content teams to pages that may need rewriting, updated SEO, better UX, or clearer topic alignment to improve performance.
Hybrid search gives CMS teams a powerful new lens for understanding their content — blending semantic meaning with structured performance data to answer questions that were previously tedious or impossible to query in SQL alone. Once this intelligence is available inside MindsDB’s Knowledge Bases, the next step is making it accessible anywhere your team works.
That’s where MindsDB’s MCP Server and Cursor's MCP Client comes in.
In the next section, we’ll show how to expose these same hybrid-search insights to natural-language queries inside Cursor — allowing developers, editors, and analysts to interact with your MySQL-backed CMS data as effortlessly as chatting with an AI agent.
From SQL to Natural Language: Using MindsDB’s MCP Server + Cursor with Your Web CMS Data in MySQL
With MindsDB’s MCP Server and Cursor’s MCP Client, your MySQL-based CMS data becomes instantly accessible through natural-language queries. Instead of writing SQL or building custom endpoints, editors, analysts, and engineers can simply ask questions—“Which articles trended last month?” or “Show posts tagged ‘AI’ with high engagement”—and get real, grounded results directly from your database. This bridges the gap between technical data access and everyday content decision-making, making AI-powered insights available to anyone on your team.
To begin, make sure you have used the below command to start the MCP server with Cursor:
docker run --name mindsdb_container -p 47334:47334 -p 47335:47335 mindsdb/mindsdb
docker run --name mindsdb_container -p 47334:47334 -p 47335:47335 mindsdb/mindsdb
docker run --name mindsdb_container -p 47334:47334 -p 47335:47335 mindsdb/mindsdb
docker run --name mindsdb_container -p 47334:47334 -p 47335:47335 mindsdb/mindsdb
Once this is up and running, you can access Cursor and follow the below instructions:
Navigate to Cursor’s Settings and open the MCP tab.
Select
Tools and MCPSelect
Add Custom MCP. It will automatically open a tab to the `mcp.json` file. Add the following details and save the changes:
{ "mcpServers": { "mindsdb": { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:47334/mcp/sse" } } }
{ "mcpServers": { "mindsdb": { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:47334/mcp/sse" } } }
{ "mcpServers": { "mindsdb": { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:47334/mcp/sse" } } }
{ "mcpServers": { "mindsdb": { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:47334/mcp/sse" } } }
Navigate back to the Cursor Settings tab and you will see MindsDB is listed under ‘Installed MCP Servers’.
Select ‘Toggle AI Pane’ and make sure the mode is set to Agent with the LLM model on Auto.
You can now start chatting with your data. Ask the Agent to access your data in the MySQL database:
1. Which authors produce the most engaging content over time?
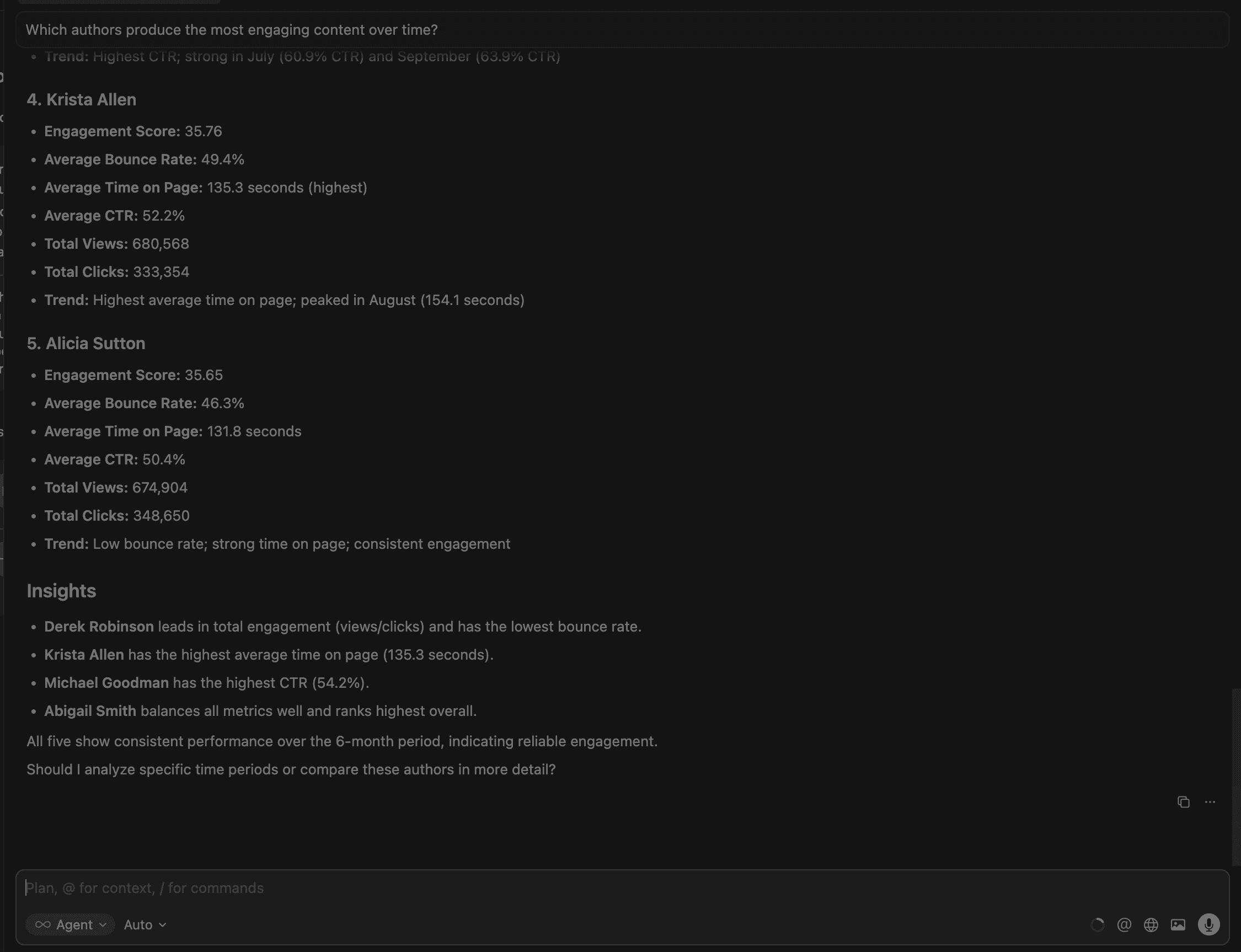
This identifies high-performing creators, helps allocate editorial resources, and informs hiring, content planning, and promotion decisions. Cursor provides the top 5 authors with their metrics,as well as detailed overall insights.
2. Which content topics or tags drive the most traffic and engagement?
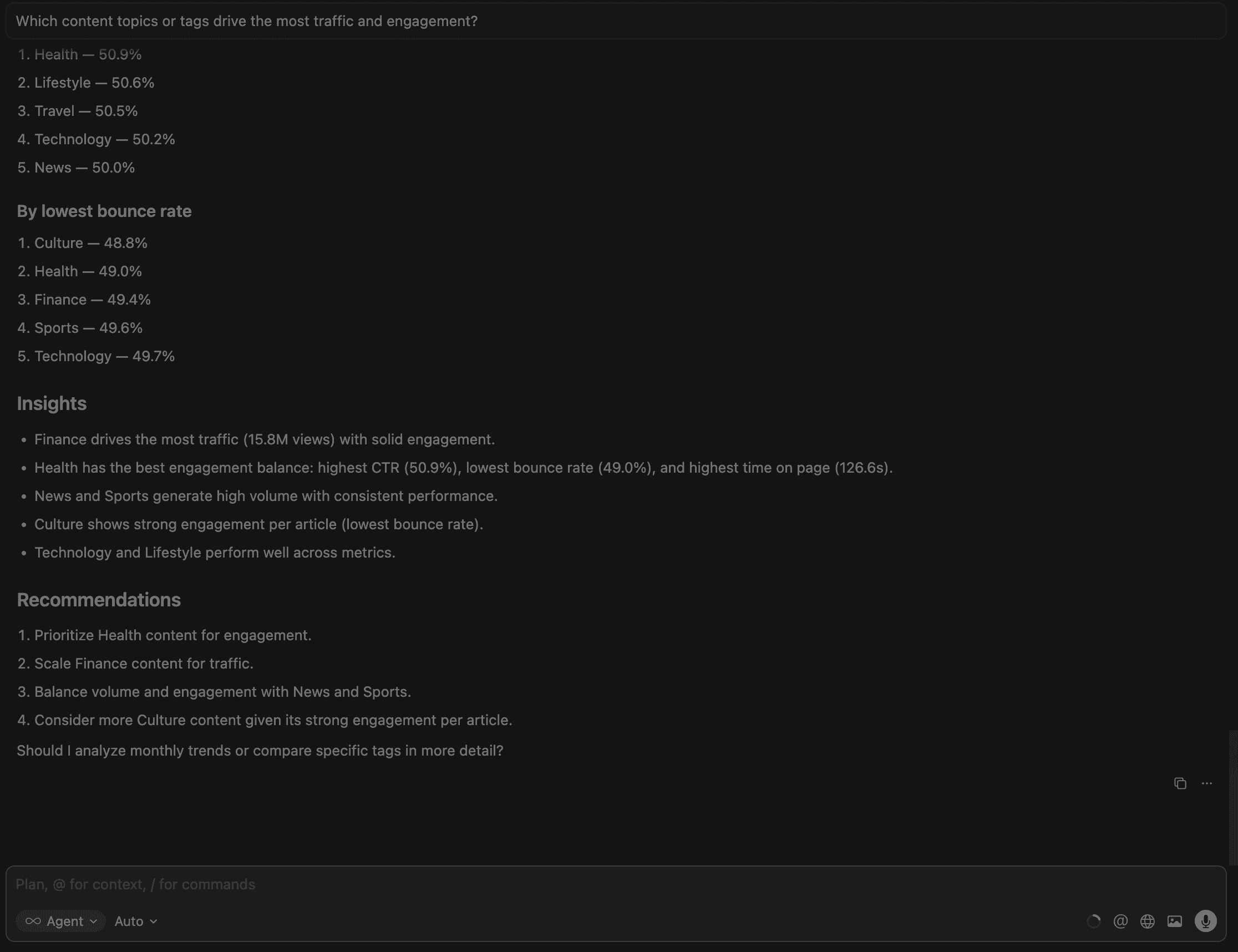
This flags content that ranks or gets traffic but fails to convert — the clearest signal for SEO optimization, rewriting, or improving titles, snippets, or structure.
3.Which articles have a high bounce rate and low engagement?
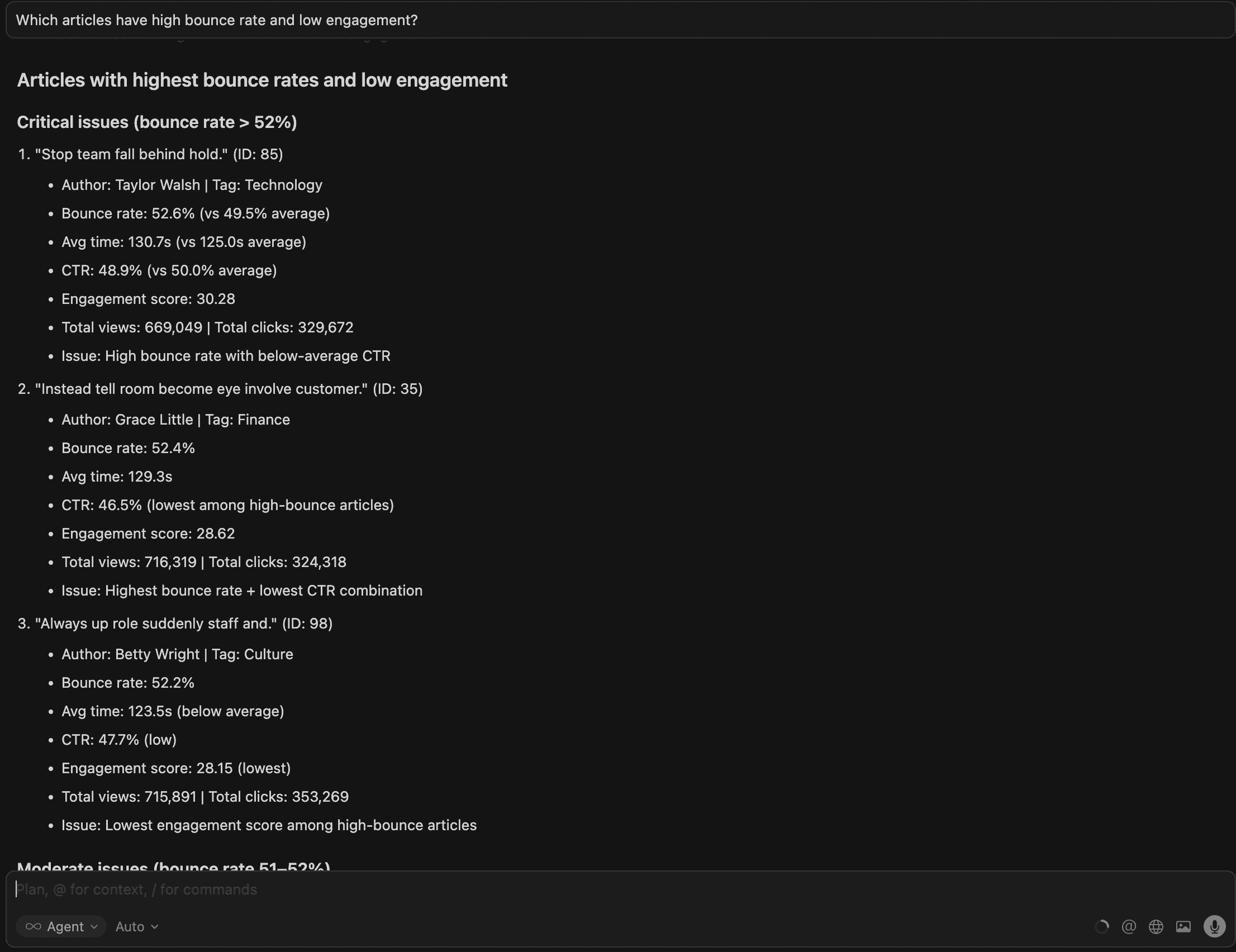
Cursor provides 8 articles with performance metrics and key patterns below.
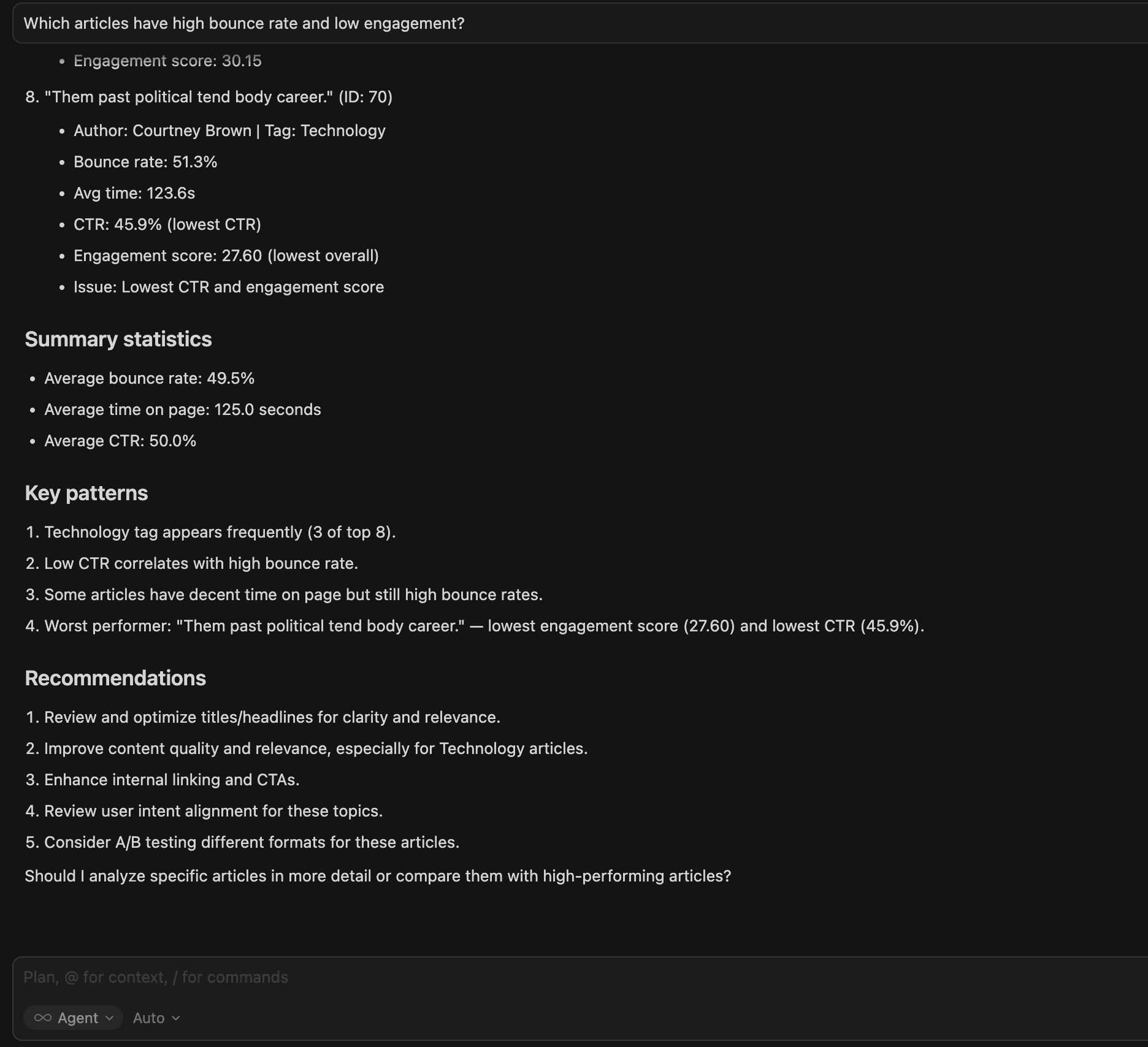
This identifies pages harming user experience and SEO quality signals; these are high-priority candidates for revision, redesign, or content replacement.
4.Which articles are trending upward or downward in performance?
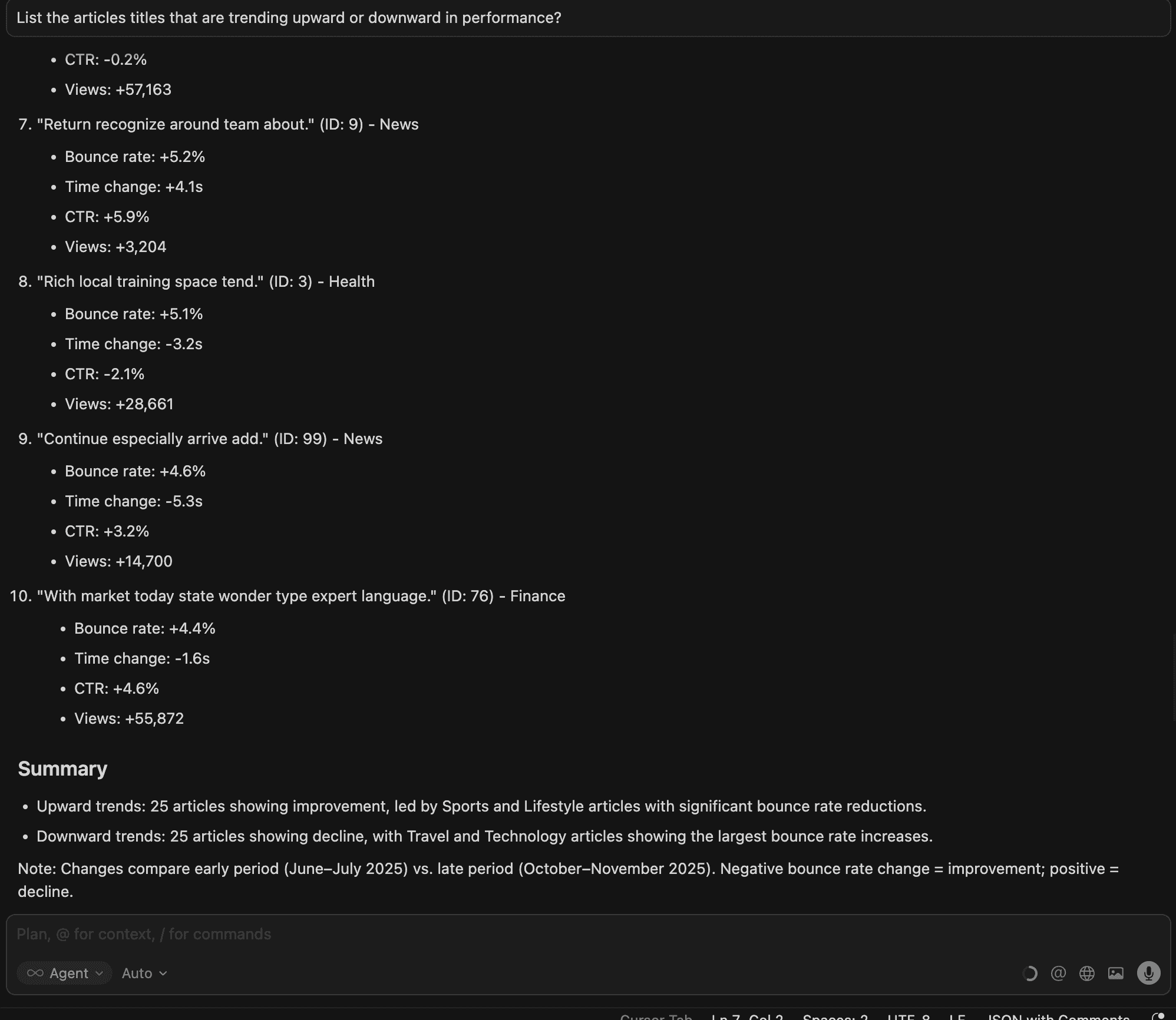
Here we can see early signals of growth or decline; essential for capitalizing on rising content and repairing slipping performers before they lose rankings.
6.Which tags or topics are underrepresented but performing strongly?
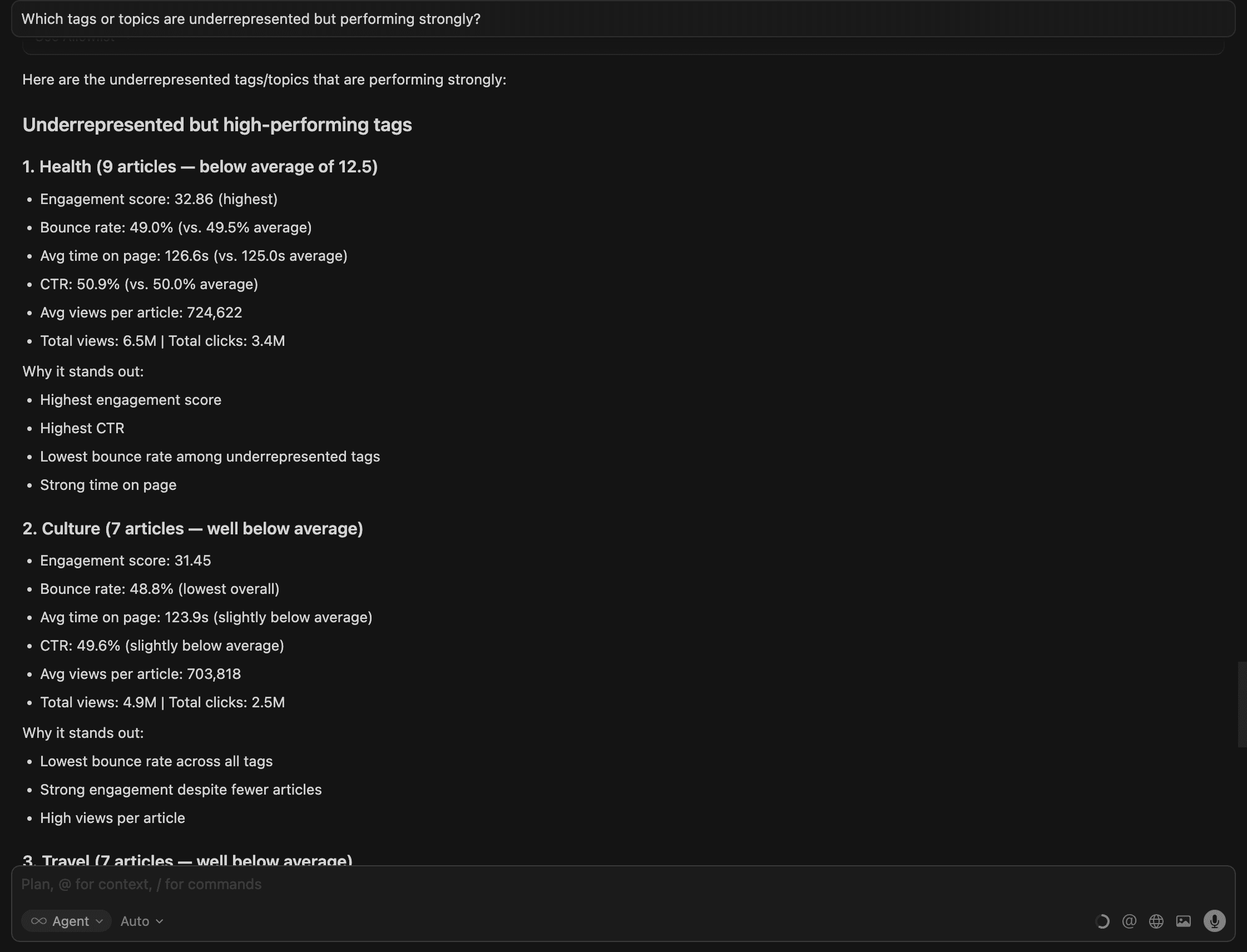
Cursor provides an overall comparison for the averages, recommendations and a summary:
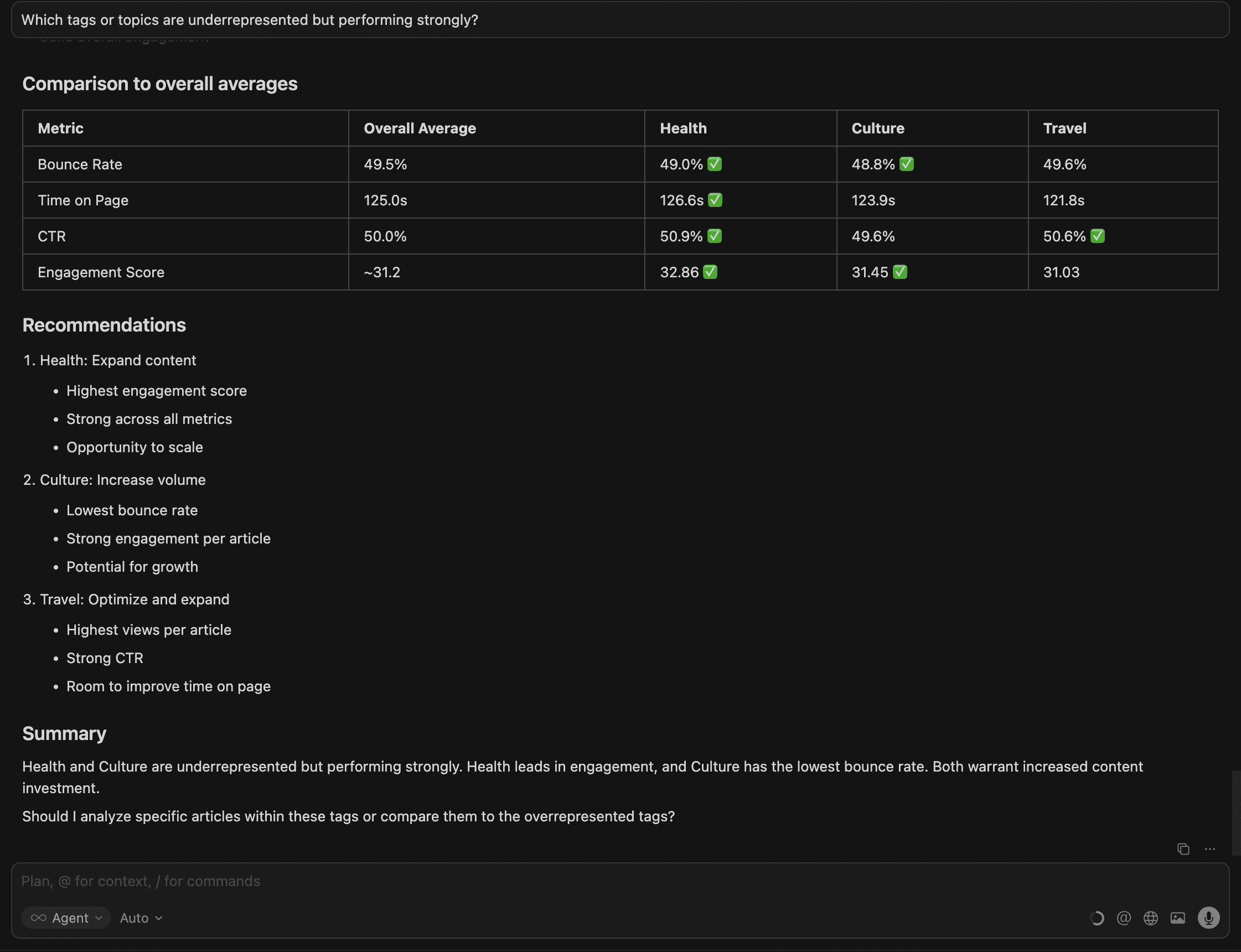
This helps teams discover high-potential opportunities — underserved content themes that deliver strong engagement and should be expanded into content clusters.
7. Which titles have strong SEO indicators based on long-term CTR trends?
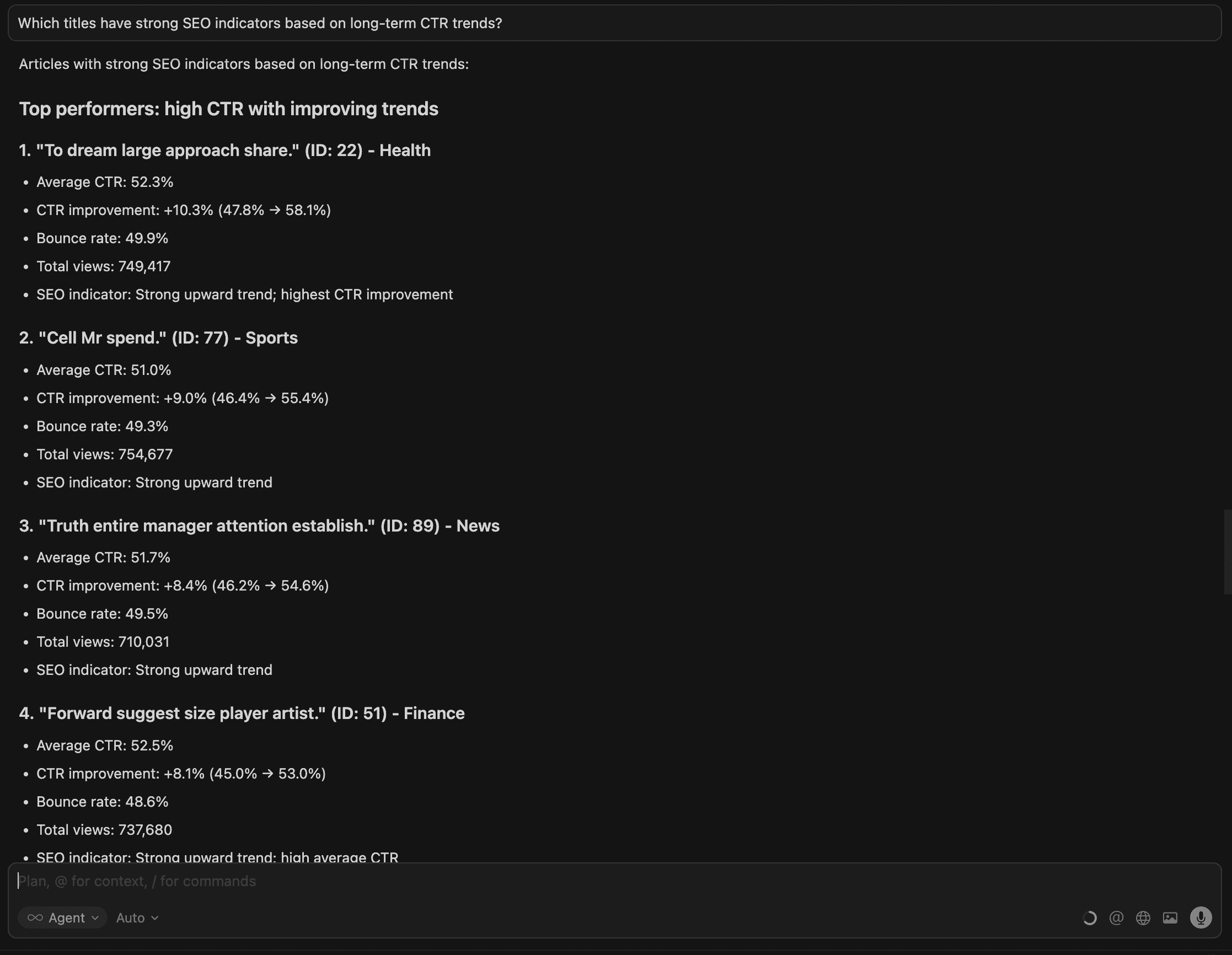
Here we get a list of articles with a summary below.
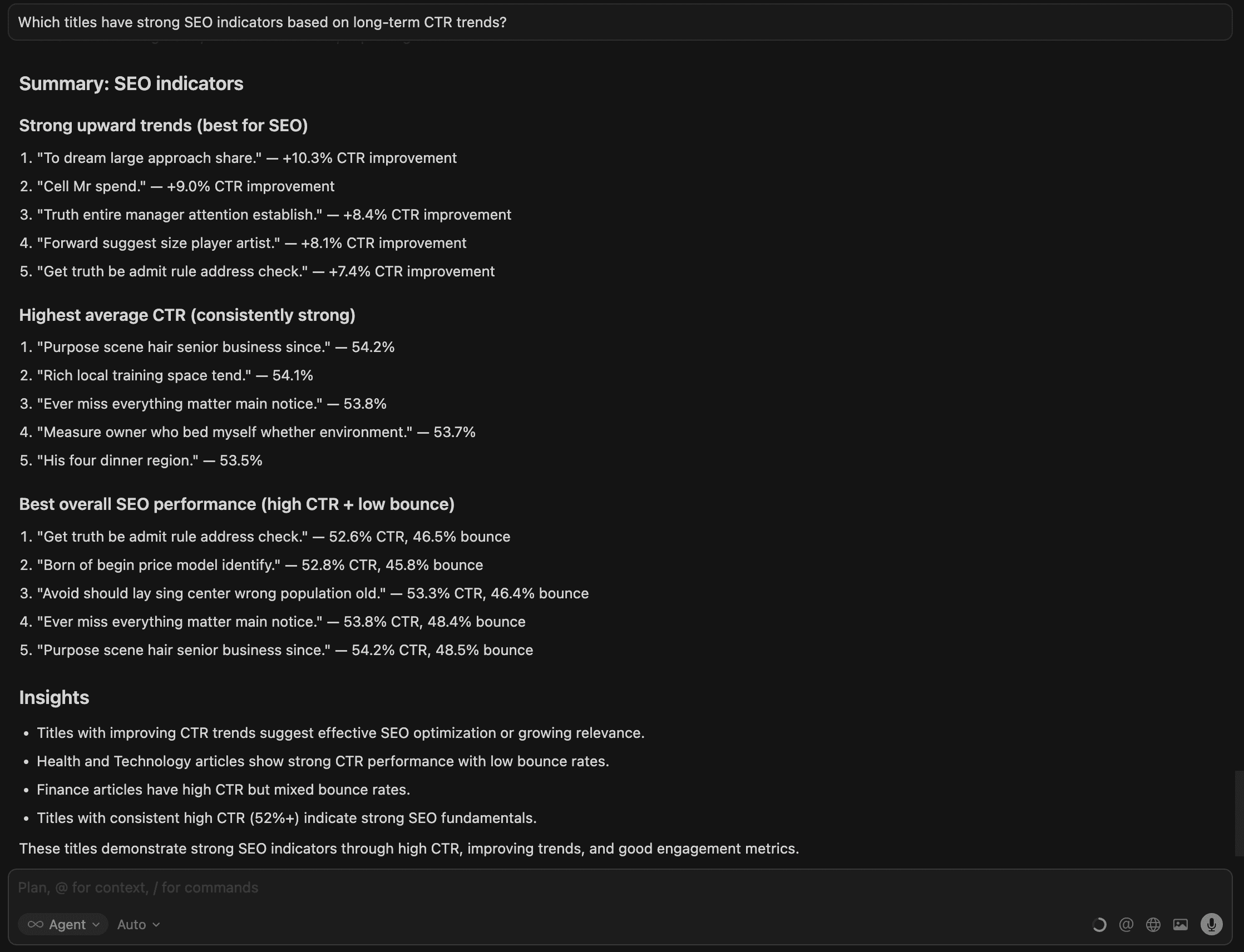
Titles with consistently strong CTR trends signal which content performs well in search over time, helping teams focus SEO efforts where it drives the most impact.
Example Use Cases Powered by MindsDB + MySQL + MCP
1. SEO Insights Assistant
Ask: “What topics performed best in October by traffic?”
How it works: MindsDB blends SQL metrics with hybrid retrieval to evaluate topic performance using both structured (views, CTR) and unstructured (content themes) data.
2. Editorial Planning Assistant
Ask: “Show me all drafts tagged ‘sustainability’ that are over 1,000 words.”
How it works: MySQL filters structured fields while Knowledge Bases surface semantic matches, helping editors plan upcoming content efficiently.
3. Content Quality & Redundancy Auditor
Ask: “Find duplicate or highly similar articles across the blog.”
How it works: Hybrid search compares article embeddings, making it easy to detect overlap, outdated pages, or pieces needing consolidation.
4. Author Performance Dashboard
Ask: “Which authors published fewer than 3 posts last month?”
How it works: MindsDB queries author output trends, enabling managers to spot gaps in coverage and support team-wide performance insights.
5. Content Gap & Opportunity Analyzer
Ask: “Which trending topics from external sources are missing on our blog?”
How it works: Combine CMS data with external knowledge sources via MCP, revealing blind spots and high-value content opportunities.
Why This Matters (and What You Gain)
Content teams rely on MySQL to store massive volumes of articles, metadata, and performance metrics — but turning that raw data into actionable insight usually requires dashboards, manual queries, or complex BI setups. MindsDB removes these barriers by letting teams search semantically, analyze trends instantly, and ask natural-language questions directly against their CMS data.
With Knowledge Bases, Hybrid Search, and MCP + Cursor:
You unlock deeper content intelligence that isn’t possible with SQL alone.
You discover patterns across topics, engagement, and SEO performance without manual digging.
You give editors, marketers, and SEO analysts AI-powered visibility into what drives results.
You connect structured (MySQL) and unstructured (content) data, enabling decisions grounded in both narrative and numbers.
You eliminate ETL and extra infrastructure, using the MySQL data you already have.
You future-proof your CMS workflow by enabling AI-native querying, automation, and discovery.
MindsDB turns your MySQL-based CMS into a real-time, AI-driven content intelligence engine — without changing where your data lives.
Conclusion
MySQL has always been the backbone of modern Web CMS platforms—reliable, structured, and central to how content teams store, organize, and publish information. But as content ecosystems grow more complex and audiences expect higher-quality, highly relevant material, traditional SQL alone isn’t enough to surface the insights teams need.
MindsDB transforms this entire landscape.
By pairing your existing MySQL data with Knowledge Bases, Hybrid Search, and MCP Server + Cursor, MindsDB turns ordinary CMS tables into an intelligent content engine—one capable of understanding semantic meaning, revealing performance patterns, and answering nuanced editorial questions in natural language.
Most importantly, you achieve all of this without moving your data, rewriting your CMS, or introducing new databases. MySQL stays your source of truth—MindsDB simply makes it smarter.
As you move forward, the combination of MySQL + MindsDB provides a scalable, future-ready foundation for content discovery, analytics, and decision-making. Whether you're running a global media operation, a SaaS documentation hub, or a content-driven startup, MindsDB helps your teams work faster, learn more, and create better content—all powered by the data you already own. If you would like to see MindsDB in action, contact our team.
Your CMS just became intelligent.
Content teams run on data — not just page views, but topic trends, engagement behavior, author performance, and semantic relationships across hundreds or thousands of articles. And most of this content lives in MySQL databases powering CMS platforms like WordPress, Ghost, Webflow, Strapi, or custom-built systems.
But while MySQL gives you structured data (titles, metadata, authors, timestamps), it wasn’t designed to answer questions like:
“Which articles discuss AI trends and have high engagement?”
“Which authors consistently publish top-performing content?”
“Show me content with a high bounce rate but low click-through rate.”
“How many blog posts relate semantically to ‘cloud security’?”
These questions require semantic understanding + structured analytics, something that traditionally requires multiple systems: ETL jobs, a separate vector database, a search index, and various analytics tools.
MindsDB removes all of that overhead by allowing MySQL data to be queried, enriched, and analyzed with AI directly — using Knowledge Bases, Hybrid Search, and the MCP Server with Cursor for natural-language access.
The Insights Content Marketing Teams Don't Have Access To
content-driven companies—from media publishers to SaaS documentation teams—run on data stored inside MySQL-based Web CMS systems. Titles, slugs, authors, tags, publish dates, engagement metrics—everything lives neatly in tables.
But the actual content—the article bodies, guides, announcements, long-form pages—lives as unstructured text. When you need to search across hundreds or thousands of pieces, traditional CMS search breaks down:
Keyword search only catches exact matches
Metadata queries can’t capture semantic meaning
Editors waste time digging for articles, reusing content manually, or re-creating pieces that already exist
AI-driven tools struggle because the CMS provides no semantic understanding
This is where MindsDB changes the game.
By connecting your MySQL CMS directly to MindsDB, you can build AI-native search, insights, and content automation—without ETL pipelines, custom vector stores, or rewriting your CMS stack.

MindsDB Bridges The Gap for Content Teams Working in MySQL
For teams managing large volumes of CMS data inside MySQL, MindsDB unlocks capabilities that traditional SQL alone cannot provide:
AI-powered insight directly on top of your existing MySQL tables — no migrations or ETL.
Hybrid Search that blends semantic meaning with precise SQL filters for richer content discovery.
Knowledge Bases that turn unstructured CMS text into searchable, analyzable AI-ready data.
Natural-language querying via MindsDB’s MCP Server + Cursor, enabling editors and analysts to “ask” questions instead of writing complex SQL.
Smarter decision-making around content performance, SEO, user behavior, and trends — all while keeping MySQL as your source of truth.
Now let’s explore how you can build an intelligent AI layer on top of your Web CMS data.

Elevate Your MySQL CMS- Unlock AI-Powered Content Intelligence with MindsDB
Now that we’ve explored why AI unlocks deeper insight from web-based content systems, let’s walk through how to actually build this inside MindsDB. In the next steps, you’ll learn how to take CMS data already stored in MySQL—titles, slugs, tags, authors, publish dates, full text—and convert it into powerful AI-ready Knowledge Bases.
To demonstrate this, we will make use of a sample Web CMS dataset hosted in MySQL.
Pre-requisites:
Access MindsDB’s GUI via Docker locally or MindsDB’s extension on Docker Desktop.
Configure your default models in the MindsDB GUI by navigating to Settings → Models.
Navigate to Manage Integrations in Settings and install the dependencies for MySQL.
After the dependencies have been successfully installed, you can connect your MySQL data to MindsDB.
You can establish a connection with MySQL using the CREATE DATABASE syntax in MindsDB’s SQL Editor:
CREATE DATABASE mysql WITH ENGINE = 'mysql', PARAMETERS = { "host": "samples.mindsdb.com", "port": 3306, "database": "public", "user": "user", "password": "MindsDBUser123!" };
You can also connect to MySQL using our GUI form:
This connection will give you access to the Web CMS data and CMS Performance Metrics data.
How MindsDB Unifies MySQL Web CMS Data with Knowledge Bases
MindsDB Knowledge Bases turn your existing CMS data into an AI-ready search and reasoning layer. Instead of treating content as plain text inside tables, Knowledge Bases enrich it with metadata, embeddings, and hybrid search capabilities. This means your articles, pages, logs, and performance metrics become semantically searchable, instantly retrievable, and usable by AI agents without moving or duplicating data.
We will make use of:
The Web CMS data that stores information about blog content
The CMS Performance Metrics which stores information about the blogs’ performances.
To start, we will create a Knowledge Base using the CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE statement:
CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE web_cms_kb USING storage = heroku.cms, metadata_columns = ['slug', 'author', 'created_at', 'updated_at', 'tags' ], content_columns = ['content'], id_column = 'title';
Here are the parameters provided:
web_cms_kb: The name of the knowledge base.storage: The storage table where the embeddings of the knowledge base is stored. As you can see we are using the PGVector database we created a connection with and provide the name orders to the table that will be created for storage.metadata_columns: Here columns are provided as meta data columns to perform metadata filtering.content_columns: Here columns are provided for semantic search.id_column: This uniquely identifies each source data row in the knowledge base.
You can insert the data using the INSERT INTO statement:
INSERT INTO web_cms_kb SELECT slug, author, created_at, updated_at, tags, content, title FROM mysql.real_cms_data;
Once inserted, you can select the data in the Knowledge Bases using the SELECT syntax:
SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb;

You can follow the same instructions to create a Knowledge Base for the Performance Metrics data:
-- Create Knowledge Base CREATE KNOWLEDGE_BASE cms_performances_kb USING storage = heroku.cms_performances_kb, metadata_columns = ['views', 'clicks', 'ctr', 'avg_time_seconds', 'bounce_rate', 'date'], content_columns = ['cms_id'], id_column = 'title'; --Insert data into Knowledge Base INSERT INTO cms_performance_kb SELECT title, `views`, clicks, ctr, avg_time_seconds, bounce_rate, `date`, cms_id FROM mysql.cms_6month_performance_metrics; -- Select Knowledge Base SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb;

Now that the Knowledge Bases are created, we can perform Hybrid Search to gain some insights.
Hybrid Search: The Missing Link Between Structured MySQL Data and AI Understanding
Hybrid Search in MindsDB brings together the best of semantic search and traditional filtering so teams can find the right content—not just content that contains matching keywords.
For MySQL-backed CMS systems, this means your content finally becomes discoverable in the way people actually search—using natural language, intent, and structured filters together.
CMS teams quickly understand how much of their content relates to a specific topic—guiding editorial planning, SEO focus, and audience targeting.
--Identify how many topics relate to a certain subject SELECT * FROM web_cms_kb WHERE content = 'food' AND hybrid_search_alpha = 0.8;
It finds all CMS articles whose content semantically relates to the subject “food”, using hybrid search to surface both direct matches and deeper contextual connections. You can identify if this topic has been explored yet.

This query returns all blog posts where the associated author consistently generates high-view content.
--Identify authors whose blogs bring in high views SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE views >= 7000 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
CMS teams can quickly identify top-performing authors, understand what drives engagement, and prioritize creators or topics that meaningfully grow traffic.

This query finds all finance-tagged blog posts that not only attract a high number of clicks but also keep readers engaged for at least 3 minutes (200 seconds).
--Identify blogs with a specific tag that have high click rate with a average reading time of 3minutes SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE tags = 'finance' AND clicks >=4000 AND avg_time_seconds >=200 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
This helps teams identify which finance-related content performs best so they can replicate or expand on successful topics.

This query identifies blog posts that lose readers quickly — high bounce rate, low click-through rate, and very short time-on-page.
--Identify blogs which has a high bounce rate and a low CTR SELECT * FROM cms_performance_kb JOIN web_cms_kb ON cms_performance_kb.id = web_cms_kb.id WHERE bounce_rate >= 0.7 AND ctr <= 0.4 AND avg_time_seconds <= 30 AND cms_performance_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5 AND web_cms_kb.hybrid_search_alpha = 0.5;
It alerts content teams to pages that may need rewriting, updated SEO, better UX, or clearer topic alignment to improve performance.

Hybrid search gives CMS teams a powerful new lens for understanding their content — blending semantic meaning with structured performance data to answer questions that were previously tedious or impossible to query in SQL alone. Once this intelligence is available inside MindsDB’s Knowledge Bases, the next step is making it accessible anywhere your team works.
That’s where MindsDB’s MCP Server and Cursor's MCP Client comes in.
In the next section, we’ll show how to expose these same hybrid-search insights to natural-language queries inside Cursor — allowing developers, editors, and analysts to interact with your MySQL-backed CMS data as effortlessly as chatting with an AI agent.
From SQL to Natural Language: Using MindsDB’s MCP Server + Cursor with Your Web CMS Data in MySQL
With MindsDB’s MCP Server and Cursor’s MCP Client, your MySQL-based CMS data becomes instantly accessible through natural-language queries. Instead of writing SQL or building custom endpoints, editors, analysts, and engineers can simply ask questions—“Which articles trended last month?” or “Show posts tagged ‘AI’ with high engagement”—and get real, grounded results directly from your database. This bridges the gap between technical data access and everyday content decision-making, making AI-powered insights available to anyone on your team.
To begin, make sure you have used the below command to start the MCP server with Cursor:
docker run --name mindsdb_container -p 47334:47334 -p 47335:47335 mindsdb/mindsdb
Once this is up and running, you can access Cursor and follow the below instructions:
Navigate to Cursor’s Settings and open the MCP tab.
Select
Tools and MCPSelect
Add Custom MCP. It will automatically open a tab to the `mcp.json` file. Add the following details and save the changes:
{ "mcpServers": { "mindsdb": { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:47334/mcp/sse" } } }
Navigate back to the Cursor Settings tab and you will see MindsDB is listed under ‘Installed MCP Servers’.
Select ‘Toggle AI Pane’ and make sure the mode is set to Agent with the LLM model on Auto.
You can now start chatting with your data. Ask the Agent to access your data in the MySQL database:
1. Which authors produce the most engaging content over time?

This identifies high-performing creators, helps allocate editorial resources, and informs hiring, content planning, and promotion decisions. Cursor provides the top 5 authors with their metrics,as well as detailed overall insights.
2. Which content topics or tags drive the most traffic and engagement?

This flags content that ranks or gets traffic but fails to convert — the clearest signal for SEO optimization, rewriting, or improving titles, snippets, or structure.
3.Which articles have a high bounce rate and low engagement?

Cursor provides 8 articles with performance metrics and key patterns below.

This identifies pages harming user experience and SEO quality signals; these are high-priority candidates for revision, redesign, or content replacement.
4.Which articles are trending upward or downward in performance?

Here we can see early signals of growth or decline; essential for capitalizing on rising content and repairing slipping performers before they lose rankings.
6.Which tags or topics are underrepresented but performing strongly?

Cursor provides an overall comparison for the averages, recommendations and a summary:

This helps teams discover high-potential opportunities — underserved content themes that deliver strong engagement and should be expanded into content clusters.
7. Which titles have strong SEO indicators based on long-term CTR trends?

Here we get a list of articles with a summary below.

Titles with consistently strong CTR trends signal which content performs well in search over time, helping teams focus SEO efforts where it drives the most impact.
Example Use Cases Powered by MindsDB + MySQL + MCP
1. SEO Insights Assistant
Ask: “What topics performed best in October by traffic?”
How it works: MindsDB blends SQL metrics with hybrid retrieval to evaluate topic performance using both structured (views, CTR) and unstructured (content themes) data.
2. Editorial Planning Assistant
Ask: “Show me all drafts tagged ‘sustainability’ that are over 1,000 words.”
How it works: MySQL filters structured fields while Knowledge Bases surface semantic matches, helping editors plan upcoming content efficiently.
3. Content Quality & Redundancy Auditor
Ask: “Find duplicate or highly similar articles across the blog.”
How it works: Hybrid search compares article embeddings, making it easy to detect overlap, outdated pages, or pieces needing consolidation.
4. Author Performance Dashboard
Ask: “Which authors published fewer than 3 posts last month?”
How it works: MindsDB queries author output trends, enabling managers to spot gaps in coverage and support team-wide performance insights.
5. Content Gap & Opportunity Analyzer
Ask: “Which trending topics from external sources are missing on our blog?”
How it works: Combine CMS data with external knowledge sources via MCP, revealing blind spots and high-value content opportunities.
Why This Matters (and What You Gain)
Content teams rely on MySQL to store massive volumes of articles, metadata, and performance metrics — but turning that raw data into actionable insight usually requires dashboards, manual queries, or complex BI setups. MindsDB removes these barriers by letting teams search semantically, analyze trends instantly, and ask natural-language questions directly against their CMS data.
With Knowledge Bases, Hybrid Search, and MCP + Cursor:
You unlock deeper content intelligence that isn’t possible with SQL alone.
You discover patterns across topics, engagement, and SEO performance without manual digging.
You give editors, marketers, and SEO analysts AI-powered visibility into what drives results.
You connect structured (MySQL) and unstructured (content) data, enabling decisions grounded in both narrative and numbers.
You eliminate ETL and extra infrastructure, using the MySQL data you already have.
You future-proof your CMS workflow by enabling AI-native querying, automation, and discovery.
MindsDB turns your MySQL-based CMS into a real-time, AI-driven content intelligence engine — without changing where your data lives.
Conclusion
MySQL has always been the backbone of modern Web CMS platforms—reliable, structured, and central to how content teams store, organize, and publish information. But as content ecosystems grow more complex and audiences expect higher-quality, highly relevant material, traditional SQL alone isn’t enough to surface the insights teams need.
MindsDB transforms this entire landscape.
By pairing your existing MySQL data with Knowledge Bases, Hybrid Search, and MCP Server + Cursor, MindsDB turns ordinary CMS tables into an intelligent content engine—one capable of understanding semantic meaning, revealing performance patterns, and answering nuanced editorial questions in natural language.
Most importantly, you achieve all of this without moving your data, rewriting your CMS, or introducing new databases. MySQL stays your source of truth—MindsDB simply makes it smarter.
As you move forward, the combination of MySQL + MindsDB provides a scalable, future-ready foundation for content discovery, analytics, and decision-making. Whether you're running a global media operation, a SaaS documentation hub, or a content-driven startup, MindsDB helps your teams work faster, learn more, and create better content—all powered by the data you already own. If you would like to see MindsDB in action, contact our team.
Your CMS just became intelligent.


